Related Articles
Exploring Progressive Churches in Houston
2 hours ago
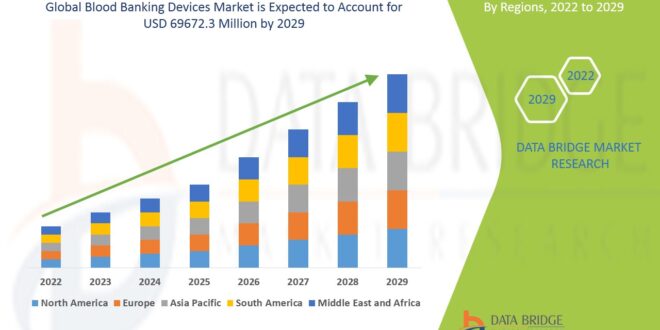
Blood banking devices play a crucial role in the collection, processing, storage, and distribution of blood and its components. These devices are essential in ensuring a safe and efficient blood supply, which is critical for various medical treatments, including surgeries, trauma care, cancer therapy, and managing chronic conditions. Blood banking has evolved significantly over the years, with advances in technology improving the safety, accuracy, and efficiency of blood collection and processing.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of blood banking devices, their functions, the technologies behind them, and their importance in modern healthcare. We will also discuss the future trends in blood banking devices and how these innovations are expected to impact the industry.
The Importance of Blood Banking
Blood is a vital resource in healthcare, used in a wide range of medical procedures. Blood transfusions can save lives during emergencies, surgeries, and for patients with chronic conditions like anemia or hemophilia. Blood banking involves collecting blood from donors, testing it for safety, processing it into various components (such as red blood cells, plasma, and platelets), and storing it until needed.
The safety and availability of blood products depend on the efficient operation of blood banking devices. These devices must ensure that blood is collected safely, processed accurately, and stored under optimal conditions to maintain its quality and prevent contamination. As such, blood banking devices are integral to the healthcare system.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-blood-banking-devices-market
Types of Blood Banking Devices
These devices can be broadly categorized into the following groups:
- Blood Collection Devices
- Blood Collection Monitors: Blood collection monitors are used during blood donation to ensure that the correct volume of blood is collected. These devices monitor the flow rate and volume of blood collected, and they can automatically stop the collection process once the desired volume is reached. This helps prevent over-collection, which can be harmful to donors.
- Apheresis Machines: Apheresis is a process that allows the collection of specific blood components, such as platelets, plasma, or white blood cells, while returning the remaining components to the donor. Apheresis machines are sophisticated devices that separate blood components in real-time during the donation process. These machines are essential for collecting high-purity blood products needed for certain medical treatments.
- Blood Processing Devices
- Centrifuges: Centrifuges are used to separate blood into its different components, such as red blood cells, plasma, and platelets. By spinning blood at high speeds, centrifuges can isolate these components based on their density. This process is critical for producing the specific blood products required for different medical applications.
- Blood Mixers: Blood mixers are used to mix blood with anticoagulants during the collection process to prevent clotting. These devices ensure that the anticoagulant is evenly distributed throughout the blood, which is essential for preserving the quality and usability of the blood during storage and processing.
- Blood Storage Devices
- Blood Refrigerators and Freezers: Blood must be stored at specific temperatures to maintain its viability. Blood refrigerators and freezers are designed to store blood products at optimal temperatures, usually between 1°C and 6°C for red blood cells and below -18°C for plasma. These storage devices are equipped with temperature monitoring systems to ensure that blood is stored safely.
- Platelet Incubators and Agitators: Platelets require special storage conditions, including constant agitation at room temperature. Platelet incubators and agitators are designed to maintain these conditions, ensuring that platelets remain viable and effective for transfusion.
- Blood Testing Devices
- Automated Blood Typing Systems: Blood typing is essential for ensuring compatibility between donor and recipient blood. Automated blood typing systems use advanced technology to quickly and accurately determine blood types, reducing the risk of transfusion reactions.
- Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT) Devices: NAT devices are used to detect infectious agents, such as HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C, in donated blood. These devices use molecular techniques to identify the genetic material of pathogens, ensuring that only safe blood is used for transfusions.
- Blood Bag Systems
- Blood Collection Bags: Blood collection bags are specially designed for safe blood collection and storage. These bags are typically made of medical-grade plastic and include anticoagulant solutions to prevent clotting. They come in different configurations, such as single, double, triple, or quadruple bags, depending on the intended use.
- Blood Transfer Bags: Blood transfer bags are used to transfer blood components between different containers or to divide a unit of blood into smaller portions. These bags are sterile and designed to maintain the integrity of the blood during the transfer process.
The Technology Behind Blood Banking Devices
Some of the key technologies used in blood banking devices include:
- Centrifugation Technology:
- Centrifugation is a critical process in blood banking, used to separate blood into its different components. Modern centrifuges are equipped with programmable settings that allow for precise control over the speed and duration of the centrifugation process. This ensures that blood components are separated efficiently and with minimal loss.
- Automation and Robotics:
- Automation plays a significant role in modern blood banking, particularly in blood testing and processing. Automated systems can handle large volumes of blood samples, perform complex tests, and process blood components with high accuracy and consistency. Robotics is also used in blood handling and storage, reducing the risk of human error and contamination.
- Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT):
- NAT is a molecular testing technology that detects the presence of viral genetic material in blood samples. This technology is more sensitive than traditional serological tests and can detect infections during the early “window period” when antibodies are not yet present. NAT has become a standard practice in blood screening to enhance the safety of the blood supply.
- Cold Chain Management:
- Maintaining the correct temperature during blood storage and transportation is crucial for preserving the quality of blood products. Cold chain management involves using specialized refrigeration equipment, temperature monitoring systems, and insulated containers to ensure that blood remains at the required temperature throughout the supply chain.
The Role of Blood Banking Devices in Modern Healthcare
Blood banking devices are integral to modern healthcare, supporting a wide range of medical treatments and emergency care. Here are some of the key roles these devices play:
- Supporting Transfusions:
- Blood transfusions are one of the most common medical procedures supported by blood banking devices. Whether for surgery, trauma care, or chronic disease management, the availability of safe and properly processed blood is critical. Blood banking devices ensure that blood is collected, tested, and stored in a way that meets the highest safety standards.
- Facilitating Organ Transplants:
- Organ transplants require precise blood matching and often involve significant blood transfusions. Blood banking devices help ensure that compatible blood products are available for transplant patients, reducing the risk of rejection and complications.
- Enabling Advanced Therapies:
- Blood banking devices also play a role in advanced therapies, such as stem cell transplants and immunotherapies. These therapies often require the collection and processing of specific blood components, which is made possible by specialized apheresis machines and other blood banking technologies.
- Emergency Preparedness:
- In times of crisis, such as natural disasters or mass casualty events, the availability of blood can be a matter of life and death. Blood banking devices help ensure that blood supplies are adequately stocked, properly stored, and quickly accessible when needed. Advanced inventory management systems and mobile blood collection units are essential tools in emergency preparedness.
Future Trends in Blood Banking Devices
Some of the key trends to watch include:
- Next-Generation Apheresis Machines:
- Future apheresis machines are expected to become more efficient and capable of collecting multiple blood components simultaneously. These machines may also incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize the collection process based on the donor’s health status and the specific needs of the blood bank.
- Artificial Blood and Blood Substitutes:
- Research into artificial blood and blood substitutes is advancing rapidly. These synthetic products could potentially reduce the reliance on donor blood, particularly in emergency situations. Blood banking devices may need to adapt to handle and store these new products as they become available.
- Blockchain for Blood Supply Chain Management:
- Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize blood supply chain management by providing a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof way to track blood products from donor to recipient. This could enhance traceability, improve regulatory compliance, and reduce the risk of fraud or contamination.
- 3D Printing of Blood Vessels and Tissues:
- Advances in 3D printing technology could lead to the creation of artificial blood vessels and tissues for transplantation. Blood banking devices may play a role in producing and storing these 3D-printed structures, particularly in ensuring their compatibility with the recipient’s blood and immune system.
Conclusion
Blood banking devices are indispensable tools in the healthcare system, ensuring that blood and its components are collected, processed, and stored safely and efficiently. These devices support a wide range of medical treatments, from routine surgeries to life-saving transfusions and advanced therapies. As technology continues to advance, blood banking devices are expected to become even more sophisticated, improving the safety, accessibility, and quality of the blood supply.
 Personal Finance and Attractive Interest Rates Unlock Smart Savings with Low Rates and Expert Financial Tips
Personal Finance and Attractive Interest Rates Unlock Smart Savings with Low Rates and Expert Financial Tips